What is Margarita Dermatitis?
What is Margarita Dermatitis?
Margarita Dermatitis, or Phytophotodermatitis, is a phototoxic inflammatory reaction caused by UVA light exposure to skin that has come into contact with certain plants. Many citrus fruits, wild vegtables, herbs and flowers can cause this painful condition. However, limes are the most common culprit, hence the name Margarita Dermatits.
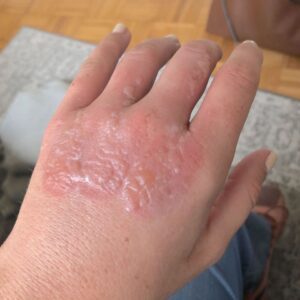
Blistering and erythema with Margarita Dermatitis
The reaction typically begins within 24 hours of exposure and peaks at 48–72 hours after exposure. The symptoms can include redness, swelling and blistering. Initially, the skin turns red and starts to itch and burn, with blisters forming about 24-48 hours after the exposure. Heat and moisture tend to exacerbate the symptoms.
Topical corticosteroids and anti-inflammatories such as aspirin or ibuprofen will help to control the symptoms. In severe cases antibiotics and oral steroids may be given.
The inflammation from the condition often causes post inflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected area. The skin develops darker patches that may require a topical skin lightening agent to reverse the effects.
Margarita dermatitis can be prevented. Avoiding contact with phototoxic botanicals when exposed to sun is the simplest way. Wear long sleeve UV protective clothing when hiking, gardening or participating in any outdoor activities where you are at risk of contact with phototoxic plants. If you are exposed wash thoroughly with soap and water, then apply a physical block sunscreen to limit the risk of an outbeak.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of Margarita Dermatitis and would like to schedule an an in-office or Telehealth evaluation, contact us.


